
Keyword Mapping: A Guide to Build an Effective Content Strategy
The right keyword is crucial to dominating online rankings.
Knowing the terms customers use online will allow you to successfully appear when they search for information on products and services, or look for your business. The right keywords matching the right page on your website could lead to conversions if those pages match users’ search intent.
But you’re competing with millions of other pages. Keyword mapping may give you an edge.
Keyword mapping is a method in search engine optimization (SEO) where you assign relevant keywords to each of the pages of your website. It maps out which particular keyword belongs to which page so that you can optimize the page and create the necessary content for it.
The goal of keyword mapping is to rank that page for its assigned keywords and avoid keyword cannibalization. It’s an effective strategy for SEO and for businesses targeting location-specific keywords to enhance local reach.
Why Is Keyword Mapping Important?
1.) It Gives Direction to Your Content Strategy
Google has indexed over 56 billion web pages, and the number continues to grow.
Choosing the right keywords is just the first step if you want your page to appear in front of your target users. The next step is to know which page the keyword is supposed to go to and then optimize that page so that it remains relevant and competitive.
Keyword mapping eliminates randomness. With it, your website and content have a direction that will help them show up more in search engines.
2.) It Helps You See Trends Across Keywords
Keyword mapping allows you to organize your keywords and pages, as well as site structure. It also helps you see trends across keywords that you would have missed if you didn’t have an organized view of the patterns that a keyword map provides. This will help you see more optimization opportunities and create better content.
3.) It Helps You Avoid Keyword Cannibalization
Google’s John Mueller says keyword cannibalization is a problem that generally occurs when you have multiple web pages targeting the same keyword phrases. It’s when the same keywords in the URL, title tag, headings, subheadings, and the content of the web page are also used in another webpage on your website.
It’s problematic because it takes away traffic from the cannibalized page and your rankings suffer as a result. So if you’re wondering why your website is losing traffic, then you may have a case of keyword cannibalization.
What Does Google Do About Keyword Cannibalization?
With Google’s Penguin update, Google could potentially see cannibalizing pages as spam and it won’t index them properly. At the same time, it would be hard for the page that you want to rank for that keyword to perform well because it’s competing with other pages on your own website.
The only course of action you can take is to choose different keywords for each web page and avoid publishing content online that has cannibalizing pages.
How Do You Use Keyword Mapping for Your Content Strategy?
There are three parts to this process: keyword research, keyword mapping, and the content strategy itself.
Step 1. Find Your Keywords
When you write an article or create a page, you must think about what you want it to rank for. Think about keywords that would be used when people are looking for similar topics.
For this, you can use Google’s Keyword Planner tool and if you’re writing a blog post, check out Yoast’s keyword research tool. It will show you where Google’s idea of your focus keyword is and how many times that word should be used.
Searching for keywords in Google will tell you what people are looking for and whether your content may be able to answer their questions. From the Keyword Planner tool, you’ll also be able to see the search volume for that specific keyword and then find out what other keywords or phrases they use.
Don’t just think about what kind of keywords you want to look for, but also think about where they’ll be placed in the article. You want them to be repeated throughout the post and not stuck up at the top with no mention again.
Checking your competitor’s site is another way to find relevant keywords. If you explore their most popular blog posts, you can probably find some keywords that would be good ideas for your own content.
For example, a web design agency may target topics like web design, graphic design, and search engine optimization. The content you’re creating must be unique with no keyword cannibalization. Product or service pages must target different keywords from those used for blog pages, and vice versa.
If you already have a page with the URL “website.com/web-design” and the page talks heavily about web design and web design services, no other page in your blog must have a similar URL or topic. Doing this could affect your page rankings and confuse your users.
Step 2. Sort Them Out and Group Them Together
Once you have identified the main category of your brand, break it down into smaller topics. List all potential topics related to your brand and what you want to focus on.
From the last example, we have three topics:
- Web Design
- Graphic Design
- Search Engine Optimization
For the purpose of this example, we’re going to try to map out keywords for blog topics revolving around web design. The process here is similar to what you would do for all pages of your website.
So imagine what your customers would be looking for, and then look for smaller topics they would likely be interested in.
Go to Google search to find keywords, or use the following keyword research tools for efficiency and better results.
1.) Google Keyword Planner
Made by Google, Keyword Planner lets you narrow down your choices by targeting or filtering results. It also shows you relevant information about the keyword, such as search volume and seasonal performance. You can use this information to strategically choose which keywords are best for your new page.
2.) Semrush
Semrush is useful in finding keywords that your website and your competitors’ websites are ranking for. You can find data such as keyword difficulty, volume, cost-per-click (CPC) stats, competitor keywords, and the number of results.
You can also assess keyword insights for both mobile and desktop indexes. They offer a paid service, but they do have a seven-day free trial so you can go ahead and see if this is a feature you could use before purchasing the product.
3.) SpyFu
SpyFu is a tool used for competitor analysis. You can monitor competitors’ keywords, including every keyword they have bought on Google and every ad variation they have used in the last decade.
For web design, we have these potential keywords:
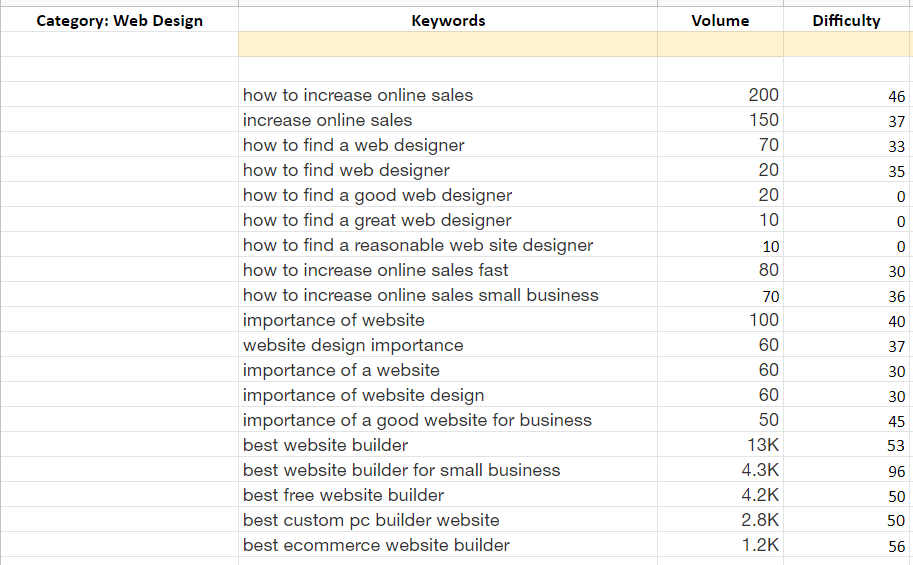
Step 3. Categorize Keywords According to Search Intent
Search intent or user intent pertains to “the why” of the user.
Begin categorizing by asking:
- Why is the user looking for a particular search query?
- What will they do after they find the query?
- Why is the user interested in consuming the content?
- What is your intention behind creating such content?
- What stage is the consumer in when it comes to the buyer’s journey?
Group your keywords accordingly.
Study your keywords and understand the relationship between your keywords and how you can target these keywords effectively so that they meet the user’s search intent.
Here are the most common types of search intent:
- Commercial: The user’s intention is to look at products and compare prices.
- Informational: The searcher aims to find information and learn more about a specific product to see if it’s the right solution to their problems.
- Navigational: The searcher is looking for a specific location or website on the internet.
- Transactional: The user is intending to buy. Some examples include booking SEO services or hiring a web designer.
To create the best content that’s optimized for the user and search engines, you must understand not only why users search for products and information but where they are in terms of the customer journey as well.
The customer journey pertains to the customer’s full experience with a brand, from awareness or brand discovery to purchasing and the process beyond that, such as customer loyalty or referrals.
The customer journey can differ from business to business; however, here is a basic example:
Awareness → Consideration → Conversion → Loyalty → Advocacy
Awareness: This is the stage where your customer is just finding out about their needs. They’re not yet aware of your product or service and might not even know everything about their problem. They are looking for information to learn more about their pain points and possible solutions to them.
Consideration: In this stage, users now have an idea and understanding of their problem and potential solutions. They are at the stage where they want to learn more about their options so that they can make more informed decisions.
Conversion: They are now ready to convert and will need more guidance on how to go about purchasing the product or service they want.
Loyalty: This is the stage where they are looking for information about what they would get if they continue purchasing the product. This could also include upsells or even a change in the subscription package.
Advocacy: This is the stage where your customers turn into brand advocates. This includes referral programs and other projects that will help your loyal customers promote your brand to others.
Consider search intent and customer’s journey when clustering your keywords or putting them into groups. This will enhance the effectiveness of your content because it will not only attract the right audience, but it will also answer relevant questions that will help funnel them down the customer journey.
Once you have your keyword groups or keyword clusters, categorize keywords that answer the same query and not have them scattered repetitively across your website.
Here’s an example of what your sheet might look like:
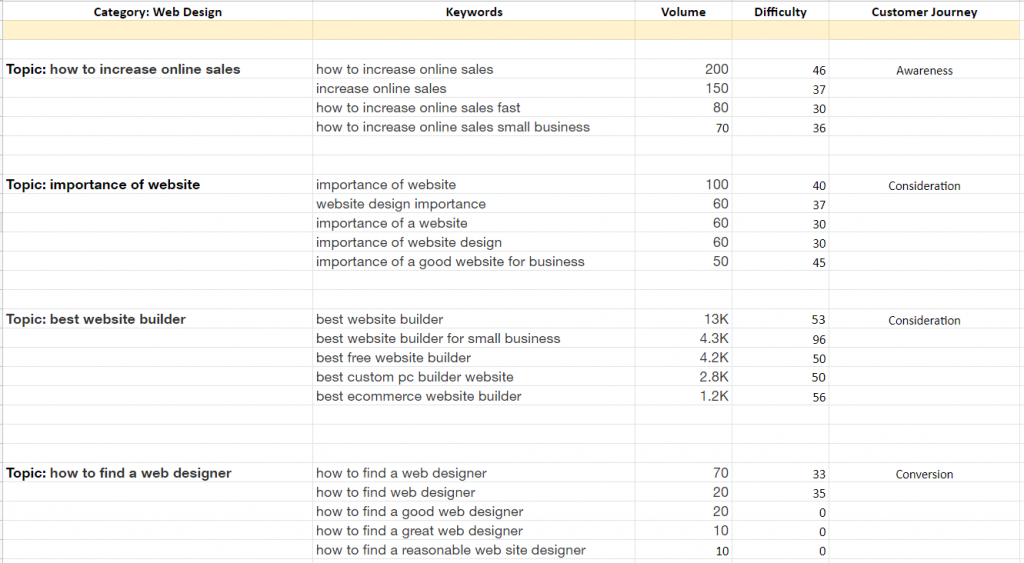
Note that since this example is designed for blog pages, the user intent is strictly informational.
Step 4. Match the Keywords to the Designated Page
After grouping the keywords, assign them their own URL.
For blogs, create a main URL for the main topic and then branch out to smaller topics using new keywords that are related to the main blog.
For other web pages, create subdirectories if necessary. This is important for retail sites with hundreds of product pages—for example, a business selling a variety of skincare products.
In the case of the example above, the sheet should look like this:
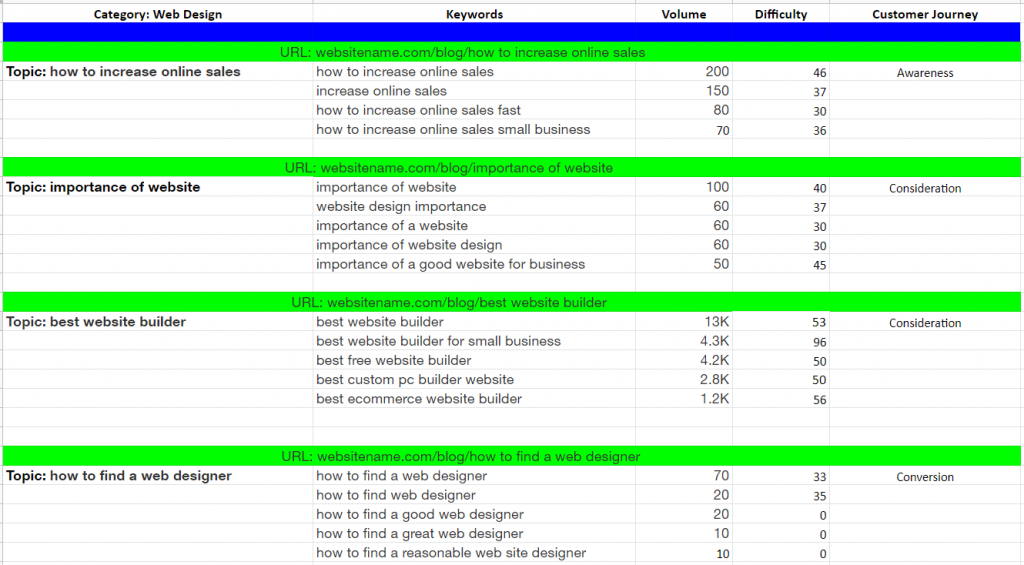
Step 5. Create or Optimize Content Using Keyword Groups or Clusters
Once you have your keywords grouped or clustered together, you now have a roadmap or framework for how you’ll create, organize, and optimize your content.
For service or product pages, create blogs that support the primary keywords you have chosen. Keep in mind that the keywords should be aligned with the search intent of the user.
For example, if you’re a dentist and you have a product page about “clear braces,” you must have a section in your keyword mapping file that looks like this:
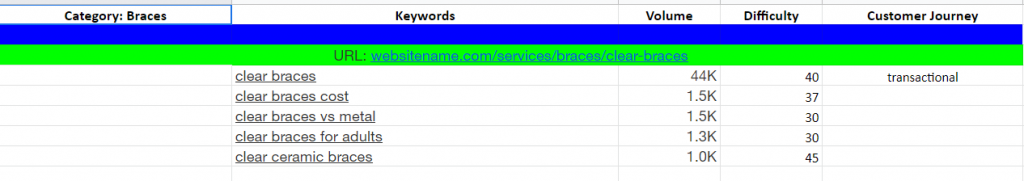
You can create a blog post to support your product page with a keyword mapping section that looks like this:
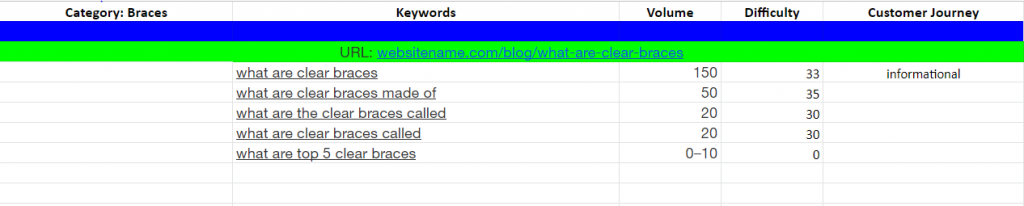
Blogs can then target informational keywords or long-tail keyword phrases. You can also create articles about questions related to your main keywords or the main page you’re trying to promote.
Pro Tip: Before creating blog content, first organize your main pages and organize your site in a structure that’s easy for the users to navigate. This means that keywords for the homepage, subdirectories, and content pages should already be defined.
Create new sheets for each page or subdirectories to keep everything accessible and organized.
Will Keyword Mapping Help My Site Rank Higher?
Keyword mapping will take a lot of work. After that, there’s the content creation process and the need to optimize your content continually so that it remains fresh and competitive.
This is an advanced SEO method that will give your business an advantage not only in search rankings but also in conversion and sales. Some SEO packages may include this method, so if you’re not up to it, go with a professional.
Technology has reached a point where search engines like Google have a greater understanding of a user’s intention, making results much more precise. So you must keep up and deliver quality, relevant, updated, and accurate information all the time.
With more and more businesses going online, invest the time, knowledge, energy, and resources to stay ahead. The results will be worth it.
Itamar Gero is the founder of SEOReseller.com, a global SEO services and digital marketing solutions provider that empowers agencies and their local clients all over the world. When he isn’t working, he’s traveling the world, meditating, or dreaming (in code).



