
Digital Manufacturing Trends in 2026: What Marketing and Operations Leaders Need to Know
Digital manufacturing isn’t a moonshot anymore; it’s infrastructure. In 2026, we have moved past the “let’s explore AI” phase and are now deep into the “let’s make this actually work” territory. The digital manufacturing trends worth paying attention to aren’t about bleeding-edge tech demos. They’re about what buyers expect, how AI is reshaping their research habits, and building experiences that not only look impressive but also convert.
Here’s what we’re seeing across manufacturing B2B: preparation beats hype, every time. The most innovative teams aren’t chasing every shiny tool; they’re aligning digital investments with what buyers need and what drives revenue. What follows isn’t speculation. It’s what’s happening right now in the companies we work with.
How AI Infrastructure Is Reshaping Manufacturing Buyer Journeys, a core thread in digital manufacturing trends
AI has become the plumbing of the buyer journey. It’s not replacing your sales engineers; it’s quietly powering search results, product recommendations, chat interfaces, and quoting tools. Think of it as the electrical system in your building: you don’t see it, but nothing works without it.
Here’s what’s actually changing:
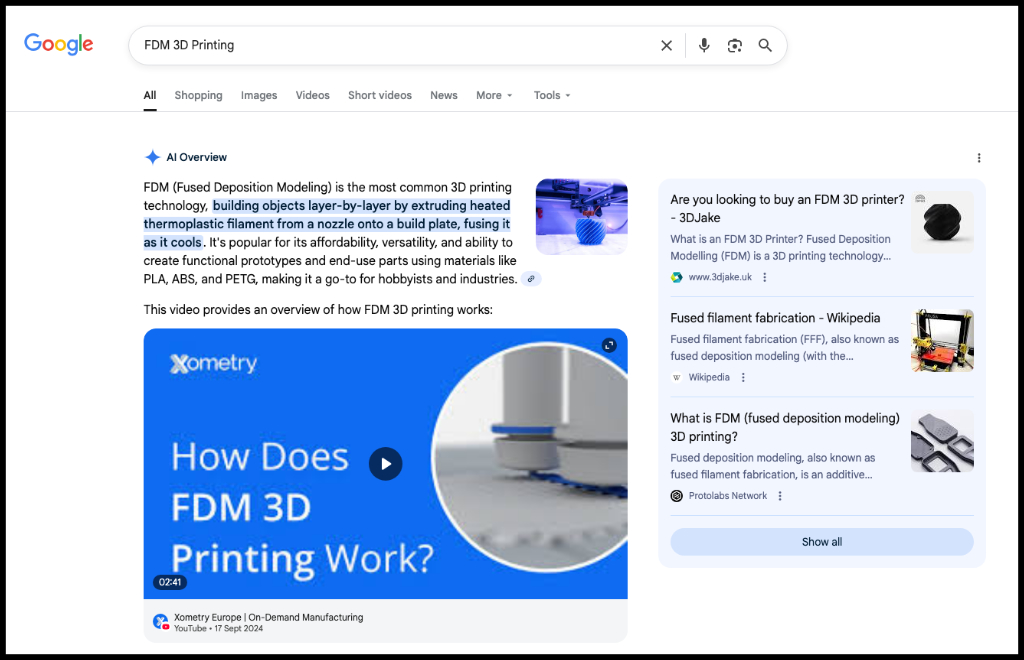
- Buyers visit Google and receive AI-generated overviews before clicking through to your site. They’re arriving more informed and expecting deeper, clearer content.
- Your website needs conversational interfaces, guided product selectors, and instant estimators that help people self-qualify without needing to pick up the phone.
- Teams are scrambling to structure their product data and tighten content governance because AI will happily serve up incorrect answers if you feed it flawed information.
Why this matters: These assistive experiences can shorten your sales cycle, improve lead quality, and build trust more quickly, but only if your content, data, and guardrails are well-defined and aligned.
AI-Powered Customer Journeys: From Static Sites to Assistive Experiences
Manufacturing websites used to be glorified brochures. Now? They’re becoming digital assistants. Buyers want to explore options, validate feasibility, and review cost estimates before speaking with anyone in sales. Many manufacturing sites still struggle with this transition, especially when navigation, content structure, and conversion paths aren’t designed for self-directed buyers.
Picture this: a chat interface asks about material requirements, tolerances, volume, and timeline. It returns an indicative price range, relevant application notes, and a button to submit drawings for engineer review. That’s not science fiction, it’s table stakes in 2026.
What buyers expect now:
- Chat support that actually understands your products and applications
- Selection wizards for materials, finishes, and configurations
- Lead-time estimators with clear “this is approximate” disclaimers
- Search that surfaces spec sheets, CAD files, and application notes instantly
The marketing takeaway? Treat AI as decision support, not a replacement for expertise. The quality of what it delivers depends entirely on structured data, clear content architecture, and knowing when to escalate to a human.
Generative Engine Optimization: Preparing Content for AI Discovery
You’ve heard of SEO. Now meet GEO, Generative Engine Optimization. It’s about creating content that AI systems can synthesize and serve up in those overview panels and chat responses. It doesn’t replace traditional SEO; it extends it.
What GEO actually requires:
- A deep library of technically accurate content: specs, tolerances, materials, process windows, QMS details, applications
- Clear structure and consistent naming (schema, relationships, entities that AI can parse)
- Visuals and files AI can interpret: drawings, photos, process diagrams, CAD, certifications
Here’s the difference: Traditional SEO focuses on chasing keywords and backlinks. GEO prioritizes comprehensive, interconnected topic coverage that answers the following three questions a buyer is likely to ask.
Build your content in clusters, process pages linked to application notes, tolerance guides, and troubleshooting documents. That way, both humans and AI assistants can assemble confident, complete answers.
As AI-driven search matures, understanding which tools actually support reliable content and discovery has become increasingly important.
Personalization at Scale: From Account-Based to Stakeholder-Based Marketing
Let’s be honest: in complex B2B cycles, “the account” isn’t one person, it’s a committee with competing priorities. ABM is evolving toward stakeholder-level engagement that respects different roles, industries, and evaluation stages.
What’s shifting:
- Personalization isn’t just firmographic targeting anymore. It’s experience-level tailoring across web, email, and sales enablement.
- Messaging gets versioned for engineers, procurement teams, quality managers, and operations, each with wildly different concerns.
- Measurement shifts from “how many MQLs?” to “are they progressing through evaluation faster and with more clarity?”
The catch? If your CRM, content, and analytics aren’t tightly integrated, personalization creates noise instead of relevance.
Hyper-Personalized ABM Execution in Complex B2B Cycles
Here’s what this looks like in practice:
Engineer-focused: “Can you hit tolerance X on material Y at volume Z?” Show SPC data, sample control plans, and design-for-manufacturability tips.
Procurement-focused: “What’s the total landed cost, lead-time variability, and supply continuity?” Show PPAP documentation, on-time performance ranges, and risk-mitigation steps.
AI and intent data can route stakeholders to the right content, but only if your CRM data is accurate and your taxonomy is consistent.
Start here: Audit your CRM fields, opportunity stages, and content tags. Define the minimum viable data for role, industry, product interest, and stage. Make it reliable before you scale automation. Otherwise, you’re just automating a mess.
First-Party Data Mastery as Competitive Advantage
First-party data powers personalization, attribution, and long-cycle nurturing. In 2026, ethical collection and precise governance are no longer nice-to-haves; they’re table stakes.
What you need to capture and keep clean:
- Role and functional priorities (engineering, procurement, quality, operations)
- Product and process interests with application context
- Content interactions tied to stage: spec downloads, tolerance calculators, portal logins
- Consent and communication preferences
Treat data strategy as infrastructure. Without governance, your advanced tactics will underperform and erode trust.
Authentic Content and Immersive Formats That Build Manufacturing Trust
Buyers are tired of marketing claims. They want to see people, processes, and tradeoffs. Short-form video and visual explainers work because they compress proof into 90 seconds: “Show me how you machine this alloy.” “Walk me through your inspection setup.” “Explain why you chose this fixture.”
Short-Form Video and Visual Storytelling in Industrial Contexts
Reels, Shorts, and YouTube work when the content is credible, not glossy. Show real operators, real machines, real decisions.
What actually works:
- 60–90-second process walkthroughs: setup, tooling, inspection
- Side-by-side comparisons: surface finish before/after, different tolerance strategies
- “What can go wrong” segments that teach and build confidence
- Voiceover CAD markups explaining manufacturability constraints
Skip the production studio. Shoot on the floor, use captions, and link to spec sheets and application notes for deeper evaluation. Authenticity beats polish every time.
Transparency and Proof Over Polish
Buyers scrutinize your expertise and how you use their data. Thought leadership needs to be grounded in demonstrated capability and an honest assessment of limitations.
Content that builds trust:
- Process capability summaries with example control charts
- Sample inspection reports and certifications with context
- Sanitized failure-mode lessons and how they informed your SOPs
- Supplier and material traceability workflows
Shift from telling to showing. Make your EEAT elements: experience, expertise, authoritativeness, trustworthiness, impossible to miss.
Data-Driven Self-Service and Portal Experiences as Marketing Assets
Self-service isn’t just a support function anymore; it shapes the evaluation process. When prospects can access documentation, view indicative pricing, and track order status, confidence increases, and sales cycles become more streamlined.
This is where data-driven marketing practices become critical. Clean CRM integration and well-defined governance enable manufacturers to personalize experiences, measure influence across extended buying cycles, and maintain buyer trust as expectations regarding data usage rise.
What buyers expect:
- Secure portals with role-based access
- Live or near-real-time order status, shipment tracking, and documentation
- Pricing visibility for standard SKUs or configurable ranges for custom work
- Asset libraries: drawings, CAD models, COAs, PPAP docs, inspection records
Your portal demonstrates operational maturity. A prospect who sees consistent lead-time updates and accessible quality documentation is more likely to trust your promises.
Treat the portal as an integral part of your buyer’s experience. Feature its capabilities on your website, integrate with CRM to inform nurturing, and create supporting content, FAQs, tutorials, and videos that help users self-serve. Balance openness with competitive sensitivity by gating sensitive assets behind verified accounts.
Integrated Digital Ecosystems: Aligning Marketing with Manufacturing Reality
As plants connect machines, quality systems, and supply data, there’s a growing risk: your website overpromises what operations can’t deliver. Digital capability only becomes a differentiator when marketing reflects real capacity, actual lead times, and honest quality practices.
Where alignment matters most:
- Lead times and capacity signals on product pages
- Quality claims mapped to actual certifications and SPC practices
- Supplier and material availability reflected in quoting expectations
- Post-sale communication integrated with portal updates and notifications
Example: If a production line is constrained, adjust quoting ranges and set expectations on the site and in nurture sequences. Nothing erodes trust faster than misalignment.
Establish a cross-functional cadence, including marketing, sales, operations, and quality, to review messaging, SLAs, and data feeds. Your Industry 4.0 maturity should match what you communicate externally.
Strategic Themes Manufacturers Must Embrace in 2026
The most durable digital manufacturing trends share a practical center: proving value, reducing friction, and earning trust with evidence.
Prioritizing Practical Over Possible
Manufacturers favor proven tools that improve lead quality, speed to quote, and sales efficiency. Evaluate investments by asking:
- Does this improve decision clarity and cycle time?
- What data and governance effort does it require?
- How complex is integration and ongoing maintenance?
- Can we measure outcomes credibly?
Anchor business cases in clear metrics and incremental wins. Pilot, measure, expand.
Resilience and Supply Chain Visibility as Differentiators
Markets remain volatile, and buyers favor partners who communicate clearly under pressure. Your digital ecosystem should emphasize:
- Transparency on lead times and constraints
- Responsiveness via portals and proactive notifications
- Data-backed reliability: on-time performance ranges, quality traceability
Build messaging frameworks around reliability proof points and keep them current as conditions change.
Core Competencies for Manufacturing Marketers in 2026
Tools evolve, but capabilities endure. High-performing teams demonstrate:
AI fluency and judgment: Know where AI assists (search, chat, routing) and where humans must lead (engineering guidance, complex tradeoffs).
First-party data mastery: Clean CRM data, clear taxonomies, and consent management to power personalization and attribution.
Execution mindset: Translate strategy into repeatable workflows, content operations, testing plans, and governance.
Cross-functional collaboration: Tight loops with sales, engineering, quality, and operations to keep promises aligned.
Continuous learning: Lightweight pilots, rapid feedback, structured retrospectives.
Start with a data hygiene sprint, content taxonomy refresh, and a small assistive experience pilot. Build a skills roadmap and training cadence.
Conclusion: Preparing for Steady Evolution, Not Disruption
Digital manufacturing in 2026 is about maturity, integration, and trust, not theatrics. These digital manufacturing trends point to a simple mandate: make it easier for buyers to discover, evaluate, and believe you.
Focus on assistive experiences, authentic content, self-service, and tight alignment with operations. Invest steadily, measure what matters, and strengthen capabilities over time.
If you’re evaluating how these digital manufacturing trends apply to your marketing strategy, we’re here to help you think through the implications. Reach out when you’re ready to talk.



